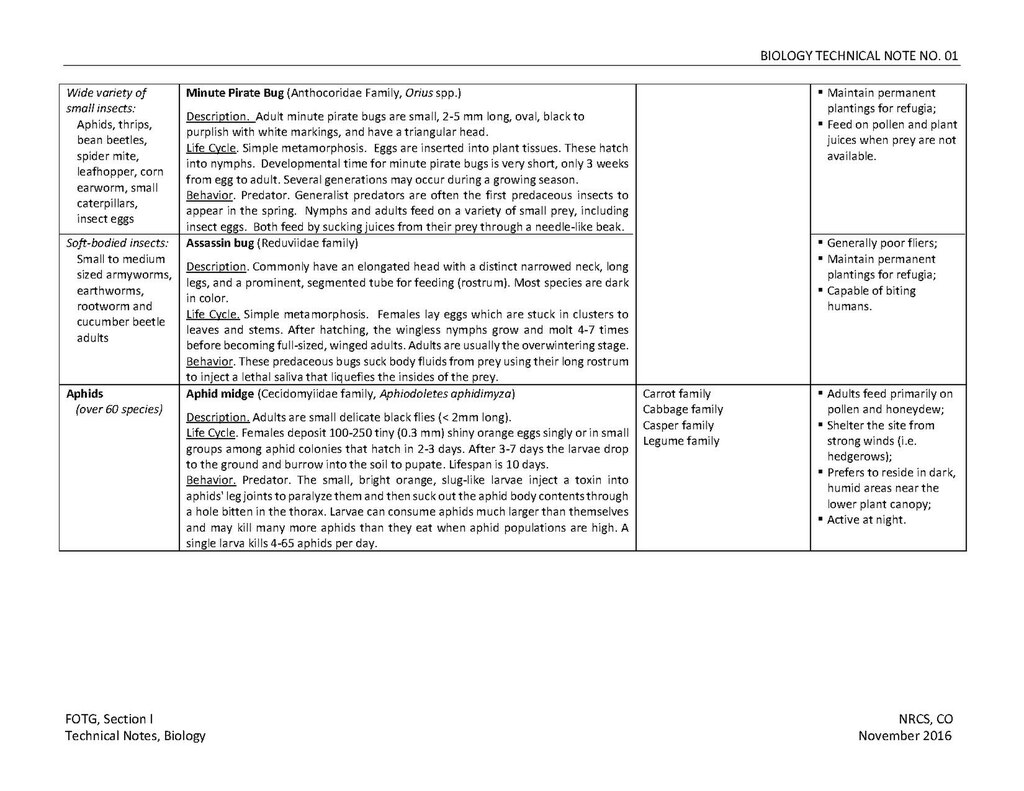
Wide variety of small insects:
- Aphids,
- thrips,
- bean beetles,
- spider mite,
- leafhopper,
- corn earworm,
- small caterpillars,
- insect eggs
|
Minute Pirate Bug (Anthocoridae Family, Orius spp.)
Description. Adult minute pirate bugs are small, 2-5 mm long, oval, black to purplish with white markings, and have a triangular head.
Life Cycle, Simple metamorphosis. Eggs are inserted into plant tissues. These hatch into nymphs. Developmental time for minute pirate bugs is very short, only 3 weeks from egg to adult. Several generations may occur during a growing season.
Behavior. Predator. Generalist predators are often the first predaceous insects to appear in the spring. Nymphs and adults feed on a variety of small prey, including insect eggs. Both feed by sucking juices from their prey through a needle-like beak.
|
|
- Maintain permanent plantings for refugia;
- Feed on pollen and plant juices when prey are not available.
|
Soft-bodied insects:
- Small to medium sized armyworms,
- earthworms,
- rootworm and cucumber beetle adults
|
Assassin bug (Reduviidae family)
Description. Commonly have an elongated head with a distinct narrow neck, long legs, and a prominent, segmented tube for feeding (rostrum). Most species are dark in color.
Life Cycle. Simple metamorhposis. Females lay eggs which are stuck in clusters to leaves and stems. After hatching, the wingless nymphs grow and molt 4-7 times before becoming full-sized, winged adults. Adults are usually the overwintering stage.
Behavior. These predaceous bugs suck bodily fluids from prey using their long rostrum to inject a lethal saliva that liquefies the insides of the prey.
|
- Generally poor fliers;
- Maintain permanent plantings for refugia;
- Capable of biting humans.
|
Aphids
- (over 60 species)
|
Aphid midge (Cecidomyiidae family, Aphidoletes aphidimyza)
Description. Adults are small delicate black flies (<2mm long).
Life Cycle. Females deposit 100-250 tiny (0.3 mm) shiny orange eggs singly or in small groups among aphid colonies that hatch in 2-3 days. After 3-7 days the larvae drop to the ground and burrow into the soil to pupate. Lifespan in 10 days.
Behavior. Predator. The small, bright orange, slug-like larvae inject a toxin into aphids' leg joints to paralyze them and then suck out the aphid body contents through a hole bitten in the thorax. Larvae can consume aphids much larger than themselves and may kill many more aphids than they eat when aphid populations are high. A single larva kills 4-65 aphids per day.
|
Carrot family
Cabbage family
Casper family
Legume family
|
- Adults feed primarily on pollen and honeydew;
- Shelter the site from strong winds (i.e. hedgerows);
- Prefers to reside in dark, humid areas near the lower plant canopy;
- Active at night.
|