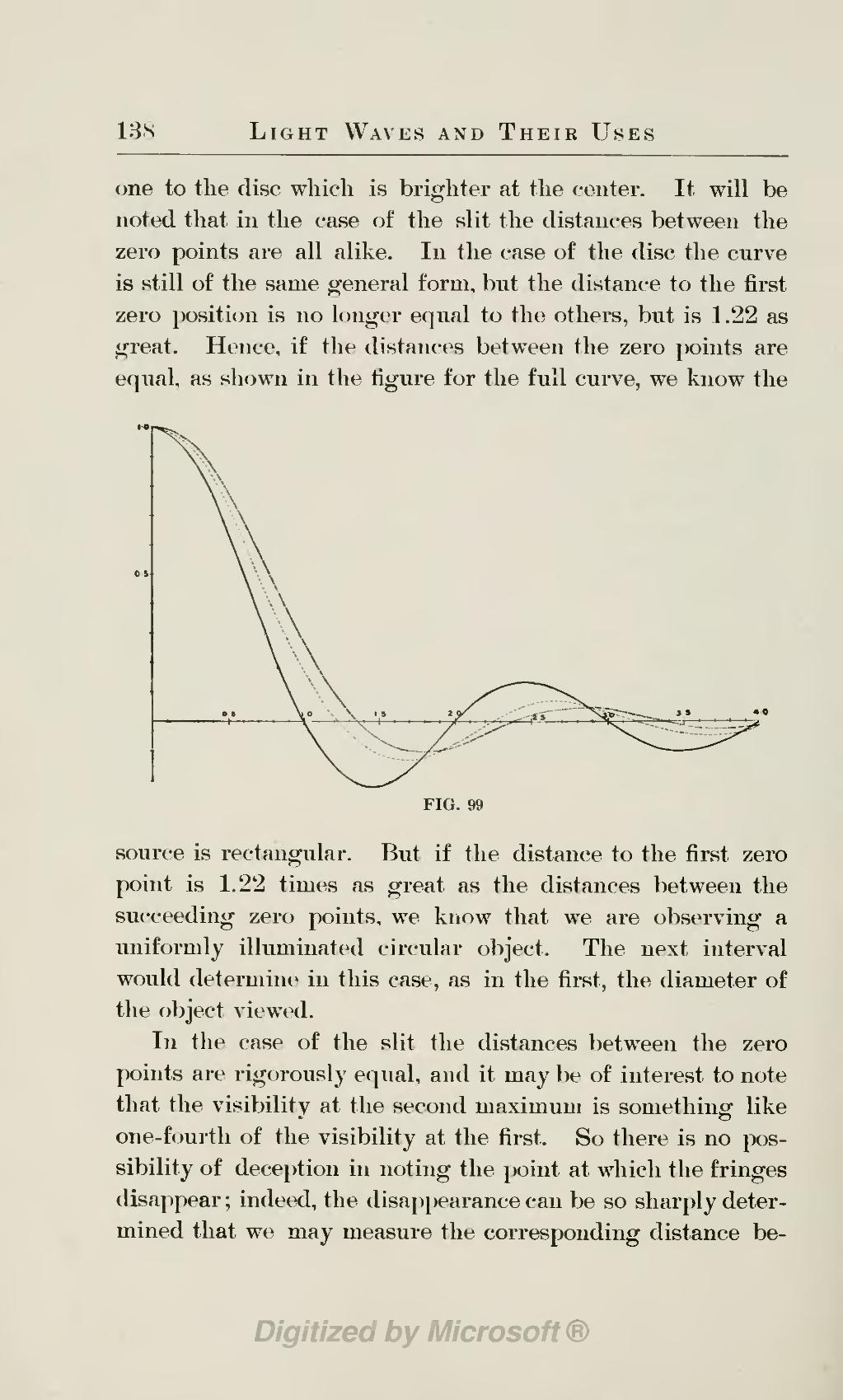
one to the disc which is brighter at the center. It will be noted that in the case of the slit the distances between the zero points are all alike. In the case of the disc the curve is still of the same general form, but the distance to the first zero position is no longer equal to the others, but is 1.22 as great. Hence, if the distances between the zero points are equal, as shown in the figure for the full curve, we know the FIG. 99 source is rectangular. But if the distance to the first zero point is 1.22 times as great as the distances between the succeeding zero points, we know that we are observing a uniformly illuminated circular object. The next interval would determine in this case, as in the first, the diameter of the object viewed.
FIG. 99 source is rectangular. But if the distance to the first zero point is 1.22 times as great as the distances between the succeeding zero points, we know that we are observing a uniformly illuminated circular object. The next interval would determine in this case, as in the first, the diameter of the object viewed.
In the case of the slit the distances between the zero points are rigorously equal, and it may be of interest to note that the visibility at the second maximum is something like one-fourth of the visibility at the first. So there is no possibility of deception in noting the point at which the fringes disappear; indeed, the disappearance can be so sharply determined that we may measure the corresponding distance be-